Prisma Finance: A new entrant into LSTFi Stablecoins
Introduction
Prisma Finance is a new LSTFi protocol that enables DeFi users to mint a fully collateralised non-custodial and decentralised dollar denominated stablecoin mkUSD using Ethereum liquid staking tokens (LSTs) as collateral. In its current form, Prisma accepts Lido’s wstETH, Coinbase’s cbETH, Rocketpool’s rETH and Frax Finance’s sfrxETH as collateral to mint mkUSD.
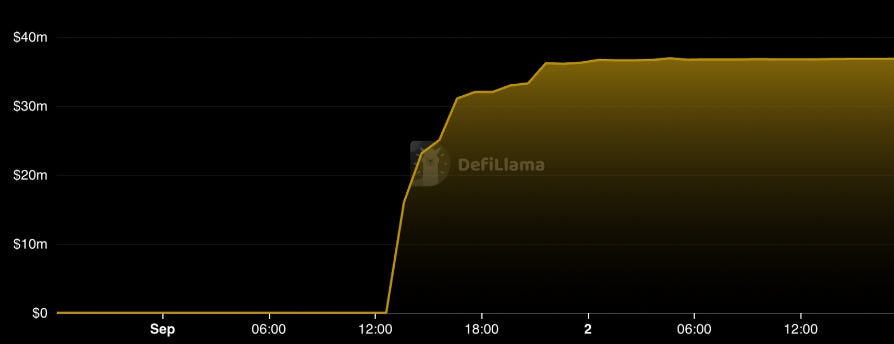
The guarded launch of Prisma on Ethereum mainnet had its debt cap hit in just 8 hours reaching a $36.8M in total value locked (TVL). The mkUSD is an overcollateralised stablecoin with a minimum-collateral ratio (MCR) of 120% that can be used to earn yield in the Prisma stability pool or in deployed Curve pools such as the mkUSD/FRAX/USDC pool to earn trading fees, CRV & CVX emissions plus PRISMA emissions. The following will provide a summary of the Prisma Finance protocol and the emerging LST-backed stablecoins vertical.
A Brief Overview of LSTFi
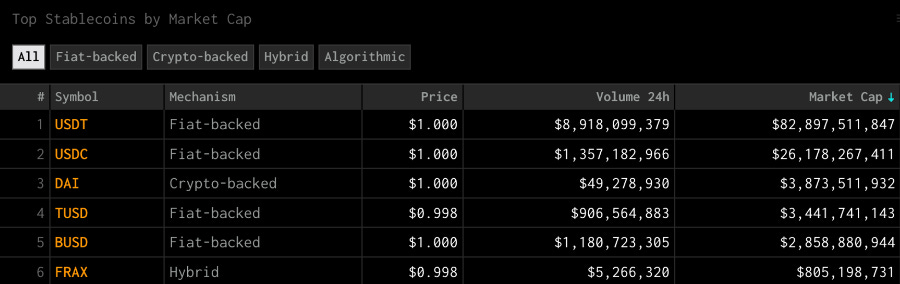
Stablecoins have arguably been the best product-market fit for crypto native settlement layers, allowing users to access a USD denominated and fully backed digital currency that bypasses the friction associated with traditional payment rails such as international settlement times and fees. Centralised stablecoins such as USDC and USDT command some of the largest market capitalisations in the digital asset space and frequently see some of the largest on-chain trading volumes.
However, centralised stablecoins suffer from custodian and regulatory risk which is the primary motivation behind the innovation in decentralised stablecoins such as DAI and FRAX. The growth of LST tokens representing the underlying yield-bearing ETH staked on the beacon chain makes them a prime candidate for eligible collateral to back decentralised stablecoins.
Prisma Finance Architecture
Prisma Finance is a Liquity inspired protocol where DeFi users can mint a decentralised stablecoin using Ethereum LSTs as collateral. To fully understand the protocol architecture, let’s take a look at the protocols execution flow:
Minting mkUSD
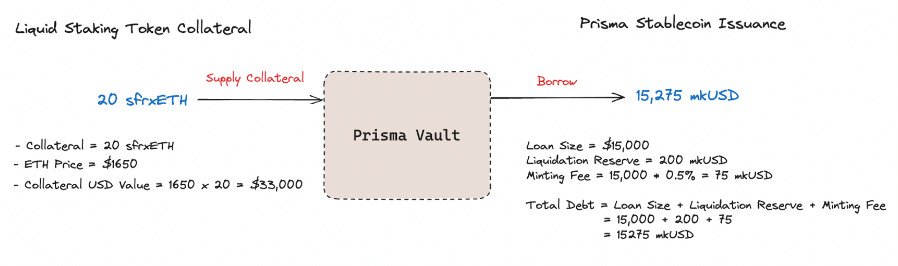
In order to mint mkUSD, users will deposit Prisma accepted collateral (wstETH, cbETH, rETH, sfrxETH) into a Prisma vault which will manage the collateral USD value and debt issued. Since mkUSD is an overcollateralised stablecoin, the minimum collateral ratio (MCR) is set at 120% before the LST loan is liquidated. The collateral ratio (CR) can be managed by users supply/removing LST collateral or repaying a portion of the mkUSD debt. The loan duration for mkUSD is indefinite and can be paid back at anytime by the borrower.
Let’s take a look at a mkUSD minting example:
DeFi user deposits 20 sfrxETH into a Prisma vault as collateral.
The user proceeds to borrow 15,000 mkUSD as their desired loan size.
Every vault deposit adds 200 mkUSD as debt which is the liquidation reserve that covers costs incurred by liquidators.
A minting fee of 0.5% is also applied to the loan which results in total debt of 15275 mkUSD to be repaid by the borrower.
Stability Pool & Liquidations
The Prisma Stability pool acts as the primary safeguard to cover the debt from liquidated vaults ensuring mkUSD is always adequately collateralised. In an event of a vault liquidation, borrowers will no longer be able to access collateral by paying off the mkUSD debt and a liquidation penalty of 16.67% is applied to the collaterals USD value.
Depositors of mkUSD in the stability pool will receive discounted collateral from vault liquidations resulting in the mkUSD balance decreasing essentially acting as a discounted value TWAP on ETH. Additionally, the Prisma stability pool is incentivised by a portion of the PRISMA emissions being directed to mkUSD depositors.
Protocol Fees
The Prisma protocol has two forms of fees applied to borrowers minting mkUSD:
Fixed Minting & Redemption Fee: A fixed minting fee applied one-time at the moment of borrowing set at a minimum value of 0.5% and maximum value of 5%. Additionally, fixed redemption fees are applied when users exchange their mkUSD for a collateral of their choice at face value.
Borrow Interest Rate: Fee that accrues over time on the outstanding debt from borrowing mkUSD. At launch the borrowing fee is set at 0% to kick start the mkUSD flywheel.
Prisma Finance Launch
Prisma Finance within the first 8 hours of launch reached the set debt cap for every deployed Prisma vault meaning the total amount of mintable mkUSD was maxed out by borrowers. The total value locked of Prisma Finance at the debt cap is standing at $38.87M.
Overtime Prisma will be slowly begin increasing the debt cap allowing more depositors to mint mkUSD as the team prepares for the launch of the PRISMA token.
mkUSD Curve Pools
There are currently two Curve pools on Curve Finance receiving directed CRV emissions:
Primsa tri-pool with mkUSD/FRAX/USDC
Prisma pool partnered with crvUSD (mkUSD/crvUSD)
These mkUSD pools are now incentivising on Convex Finance allowing liquidity providers to stake their LP tokens to earn CVX rewards and eventually PRISMA emissions.
PRISMA Tokenomics
The PRISMA token is primarily a governance token to decentralise the Prisma protocol over time allowing token holders to vote on governance proposals to collectively upgrade the Prisma protocol. In order to participate in protocol governance, PRISMA holders must lock their tokens in order to receive voting power. PRISMA locking works as follows:
User locks PRISMA for a certain duration and the max duration being 52 weeks.
Users can extend, split, merge and freeze existing PRISMA locked durations.
Early PRISMA withdrawals are subject to a linear decaying withdrawal fee.
Beyond protocol Governance the PRISMA token can be used for the following functionality:
PRISMA Emission Voting: PRISMA lockers can vote on where PRISMA emissions are directed. Emissions can be directed to the stability pool, staking Curve LP tokens, minting new mkUSD and maintaining mkUSD debt.
Emissions Boosting: PRISMA lockers are eligible for boosted emissions capped at 2x that is distributed to borrowers.
DAO Voting: Admin voting for controlling fees, adding/removing eligible collateral, pausing protocol functionality and adjusting vote quorum.
Risks in LSTFi Stablecoins
There are some issues associated with overcollateralised stablecoins in their design with respect to scalability. In general, the growth of overcollateralised stablecoins is limited by the inherent demand to get leveraged long ETH on-chain. Prisma requires large collateral ratios often >200% to avoid liquidation. Others risks include:
Several LSDFi stablecoins creates liquidity fragmentation and thus makes the defensibility of the USD peg more difficult.
There are already several LSD-backed stablecoins live on the market such as DAI, Lybra Finance and crvUSD. Hence, Prisma Finance does not benefit from a first mover advantage.
Summary
Prisma Finance has had a successful launch on Ethereum mainnet maxing out the set debt cap within 8 hours of deployment commanding a TVL of $37M. LSTFi offers alternatives to centralised stablecoins but are ultimately a function of the demand that DeFi users want to get levered long on their LST holdings and earn additional yield in the DeFi application layer.
There are already similar competitors in the LSDFi vertical such as Lybra Finance, crvUSD and DAI. Hence, finding a defensible moat will prove to be difficult given Prisma does not have the first mover advantage. We will be keeping a close eye on mkUSD growth in relation to other LST-backed stablecoins and how defensible the mkUSD peg is over time.